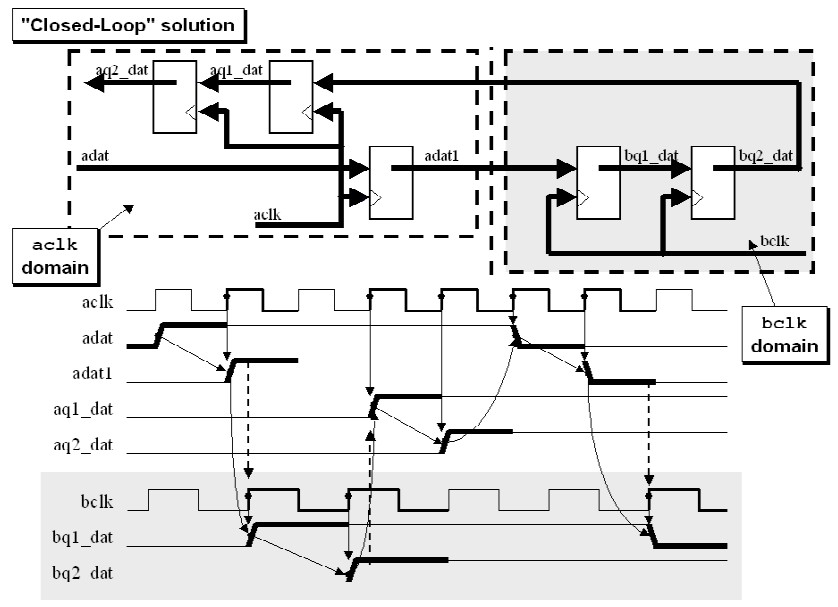
A closed-loop solution is a safer and more robust approach for Clock Domain Crossing (CDC) synchronization compared to the open-loop method.
In this design:
- An enabling control signal is sent from the source (sending) clock domain.
- The control signal is synchronized into the destination (receiving) clock domain.
- Once recognized, an acknowledgment (ACK) signal is generated in the destination domain.
- The ACK signal is then synchronized back through another synchronizer into the sending domain, confirming that the signal was successfully received.
This creates a feedback loop between the two clock domains.
🔄 Signal Flow Overview
✅ Advantages
-
High reliability:
The use of a synchronized feedback acknowledgment signal ensures that the original control signal has been safely received and sampled in the destination domain. -
Automatic compliance:
The closed-loop design inherently satisfies the “three-edge” requirement, since the sender waits for confirmation before toggling the signal again.
⚠️ Disadvantages
-
Increased latency:
The control signal must be synchronized in both directions (send and acknowledge).
This introduces considerable delay before the signal can change again. -
Lower throughput:
Because the sender waits for acknowledgment, this method is slower compared to the open-loop solution.
🧩 Summary
| Aspect | Closed-Loop Solution |
|---|---|
| Speed | Slower (due to acknowledgment delay) |
| Reliability | Very high |
| Design Type | Feedback-based |
| Use Case | When timing relationships are unknown or vary |
| Best Practice | Ideal for asynchronous or variable-frequency systems |